Understanding and Reducing Human Impact on the Environment: Causes, Effects, and Actionable Solutions

Photo by Colin Chadwick on Unsplash
Introduction
Human activities have transformed the environment on a global scale, affecting ecosystems, climate, and biodiversity. While progress in agriculture, industry, and urban development has improved lives, it has also led to significant negative environmental consequences. Understanding these impacts is critical for adopting effective solutions and making more responsible choices in daily life. This article explores the main ways humans negatively affect the environment, with detailed explanations, current examples, and actionable steps to reduce your own impact.
Deforestation and Habitat Destruction
Deforestation involves the removal of forests for agriculture, urban development, and resource extraction. Since 2001, approximately 220,000 square kilometers of forest have been lost each year, primarily due to logging, agricultural expansion, and infrastructure projects. This loss of tree cover reduces vital carbon sinks that absorb greenhouse gases, increases local temperatures, and leads to biodiversity decline. For example, the conversion of Indonesian rainforests for palm oil production has displaced endangered species and altered regional climates. The effects are global: less forest means less carbon sequestration, more greenhouse gases, and weakened resilience to climate change [1] .
How to Take Action: Support certified sustainable wood and paper products, reduce paper waste, and choose products made from recycled or responsibly sourced materials. If you want to get involved in reforestation, look for local conservation groups or international organizations with verified track records.
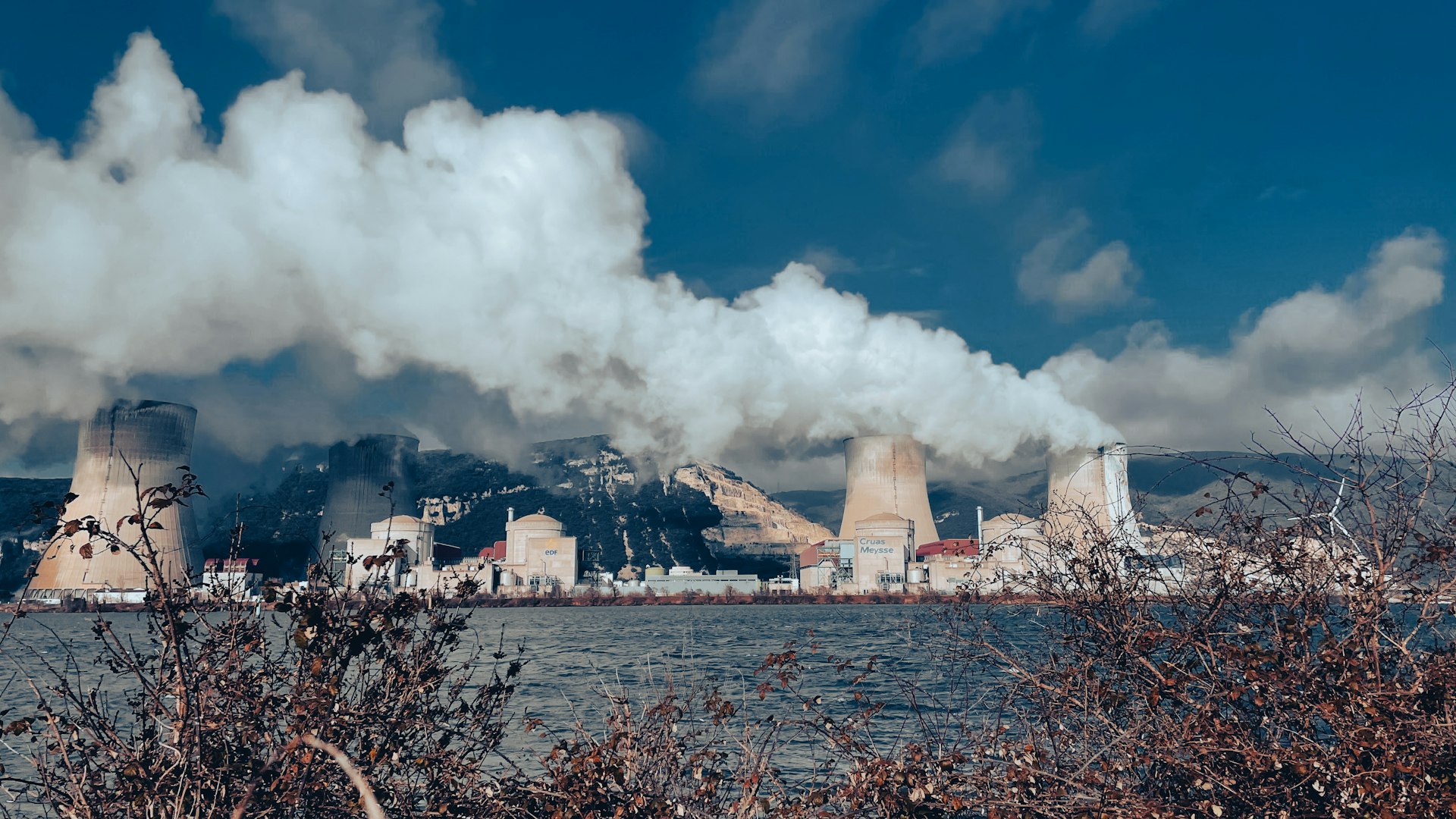
Fossil Fuel Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The burning of coal, oil, and natural gas for energy is the single largest source of global greenhouse gas emissions, responsible for over 75% of the total. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap heat in the atmosphere, driving global warming and causing extreme weather, rising sea levels, and ecosystem disruption. The average global temperature has risen by about 1.1°C since the late 19th century, leading to more frequent heatwaves, droughts, and floods [1] [2] .
How to Take Action: Reduce energy use by upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, using public transport, and supporting policies or providers that invest in renewable energy. If you’re interested in clean energy options, contact your energy supplier to ask about green tariffs or community solar programs. For transportation, consider carpooling, biking, or purchasing a hybrid or electric vehicle if feasible.
Industrialization, Pollution, and Waste Management
Industrial processes contribute to pollution through the release of toxic substances into air, water, and soil. Air pollution from factories and vehicles affects human health and ecosystems. Waterways are often contaminated by industrial waste, untreated sewage, and runoff from agriculture, harming aquatic life and making water unsafe for humans. Solid waste from overproduction and overconsumption, especially non-biodegradable materials like plastics, accumulates in landfills and natural environments, releasing harmful chemicals as they degrade [3] [4] .
How to Take Action: Reduce, reuse, and recycle wherever possible. Properly dispose of hazardous materials (like batteries and electronics) by locating certified collection points; many local governments provide these services. You can also support companies that prioritize sustainable packaging and transparent waste management practices.
Agricultural Practices and Soil Degradation
Modern agriculture, especially intensive monoculture, overgrazing, and heavy use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, degrades soil quality, reduces biodiversity, and contributes to water pollution. Cotton, for example, uses 6% of all pesticides and 16% of insecticides globally. Livestock farming is the leading user of agricultural land and is responsible for significant greenhouse gas emissions, mainly methane [4] .

Photo by Daria Trofimova on Unsplash
How to Take Action: Choose organic or sustainably produced food and textiles when possible. Support local farmers’ markets and Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) programs. Reduce food waste by planning meals and composting organic scraps. If you are a landowner, consider implementing crop rotation, cover cropping, or other regenerative agriculture practices. For more information on sustainable agriculture, contact your local cooperative extension or agricultural university.
Water Pollution and Contamination
Water resources are polluted by industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and improper waste disposal. This impacts aquatic ecosystems, disrupts food chains, and poses health risks to communities lacking safe drinking water. For example, microplastics from synthetic fibers and toxic chemicals from textile dyes can contaminate rivers and oceans, harming wildlife and people. According to the World Health Organization, about 2 billion people lack access to safe drinking water, increasing the risk of diseases like cholera and hepatitis A [4] .
How to Take Action: Avoid disposing of chemicals and pharmaceuticals down the drain. Choose natural cleaning products and support brands with water stewardship commitments. If you live in an area with industrial activity, check with your local health department for water quality reports and filtration guidance.
Overfishing and Unsustainable Resource Use
Overfishing and industrial-scale livestock farming disrupt ecosystems and deplete renewable resources. Unsustainable fishing practices destroy marine habitats and threaten species with extinction. Livestock farming accelerates deforestation and soil degradation. Fast fashion and overproduction in manufacturing generate vast waste, including non-biodegradable materials that persist in landfills and waterways for centuries [4] .
How to Take Action: Choose sustainably sourced seafood-look for certifications such as Marine Stewardship Council (MSC). Reduce meat and dairy consumption, or seek out products labeled as pasture-raised or certified humane. For clothing, buy fewer, higher-quality garments and avoid fast fashion brands. Engage in local clean-up initiatives or conservation programs focusing on habitat restoration.
Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Urban growth often leads to the removal of natural vegetation, the expansion of road networks, and increased impermeable surfaces. This causes habitat loss, greater stormwater runoff, and higher risks of flooding and erosion. Infrastructure projects can fragment habitats and open up remote areas to exploitation, further threatening wildlife and ecosystems [3] .
How to Take Action: Support urban greening projects, tree planting events, and initiatives that promote green roofs or permeable pavements. If you’re a homeowner, plant native species in your yard and minimize impervious surfaces. Encourage local governments to prioritize sustainable development and smart growth policies through public comment periods or community meetings.
Challenges and Solutions
Addressing humanity’s negative impacts on the environment requires collective action, government policy, and individual choices. Challenges include economic pressures, lack of awareness, and resistance to change. Solutions include adopting sustainable consumption habits, supporting responsible businesses, advocating for stronger environmental regulations, and participating in local conservation efforts. Education is critical-learning more about your local environment and sharing this knowledge can inspire wider action.
If you’re unsure where to start or how to get involved, consider contacting your local environmental agency, searching for non-profit organizations specializing in conservation, or attending educational workshops on sustainability. Many universities, libraries, and community centers offer resources and events to help you learn more and take effective action.
References
- [1] Climate Impacts Tracker (2024). Human activities that affect the environment.
- [2] Impact Day (2023). 10 Negative Impacts of Humans on the Environment.
- [3] Office of the Auditor General of Canada (2021). Human Activities and their Potential Impact on the Environment.
- [4] Project Cece (2022). Human Activities That Affect the Environment.
MORE FROM promohunterpro.com