Is Coal Good for the Environment? The Environmental and Health Impacts of Coal Use

Photo by Klim Musalimov on Unsplash
Introduction
Coal has been a cornerstone of global energy production for centuries, valued for its abundance and relatively low cost. However, growing concerns about climate change, air quality, and public health have put coal’s environmental impacts under scrutiny. This article examines whether coal is good for the environment, detailing its effects on air, water, ecosystems, and human health, as well as the regulatory and technological measures to mitigate its harm.
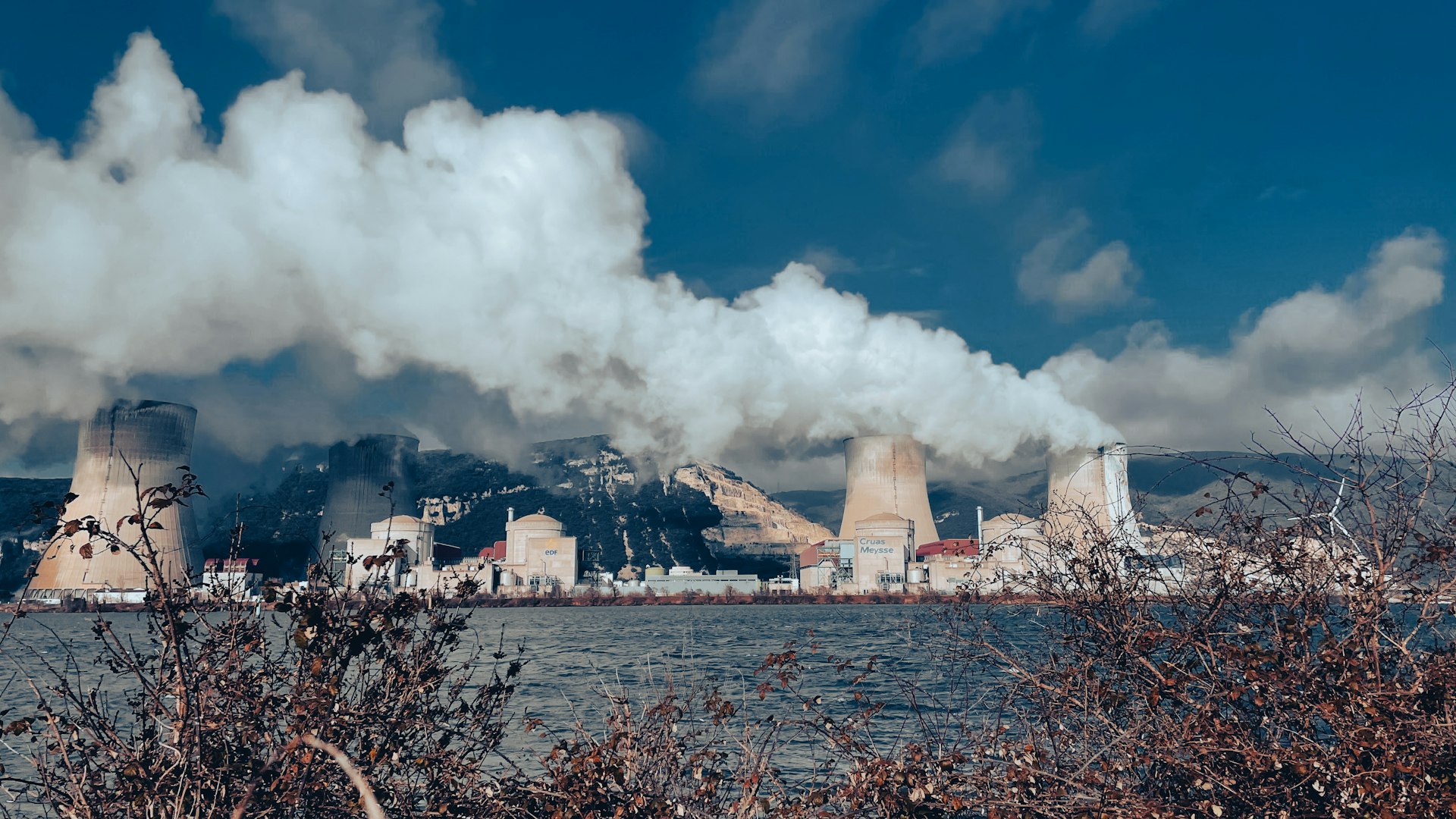
Environmental Impacts of Coal
Air Pollution and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Burning coal for electricity is a major source of air pollutants, including sulfur dioxide (SO
2
), nitrogen oxides (NO
x
), particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), mercury, and heavy metals
[2]
. These pollutants contribute to smog, acid rain, respiratory illnesses, and even neurological damage
[2]
.
Coal combustion is also a leading source of carbon dioxide (CO
2
), the primary greenhouse gas driving climate change. In 2022, coal accounted for about 19% of total U.S. energy-related CO
2
emissions and 55% of CO
2
emissions from the electric power sector
[2]
. This makes coal a major contributor to global warming.
Health Risks from Coal Pollution
Coal-fired power plants are linked to significant health risks. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from coal is especially dangerous, with studies showing it is associated with more than double the risk of mortality compared to PM2.5 from other sources [1] . Recent research estimates that 460,000 deaths in the U.S. between 1999 and 2020 were attributable to coal PM2.5, with most occurring before 2007 when coal pollution was at its peak [1] .
Exposure to coal-related air pollution is associated with asthma, cancer, heart disease, lung ailments, and neurological problems [4] . Children, the elderly, and people with pre-existing conditions are particularly vulnerable.
Mining and Land Use
Coal mining, especially surface mining and mountaintop removal, drastically alters landscapes and ecosystems. These practices can destroy forests, bury streams, and contaminate water supplies with heavy metals and acid mine drainage [2] . Even with reclamation efforts, the ecological damage is often long-lasting.
Underground mining poses risks of land subsidence and methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. Methane from active and abandoned coal mines accounted for about 7% of total U.S. methane emissions in 2021 [2] .

Photo by Trung Nguyen on Unsplash
Waste and Water Contamination
Coal combustion produces large amounts of ash, which contains toxic substances like arsenic, lead, and mercury. While pollution controls capture most fly ash, improper storage can lead to groundwater contamination and catastrophic spills [2] .
Regulatory and Technological Responses
Pollution Control Technologies
Scrubbers (flue gas desulfurization systems), electrostatic precipitators, and baghouses are used to reduce sulfur dioxide, particulates, and heavy metals from coal plant emissions [2] . These technologies have significantly reduced coal-related air pollution in the U.S. since the early 2000s.
Policy and Market Shifts
Stricter environmental regulations, competition from natural gas and renewables, and declining coal demand have led to the closure of many coal plants. By 2020, deaths attributable to coal PM2.5 in the U.S. had dropped about 95% from their 1999 peak [1] . Despite this progress, coal still poses environmental and health risks, especially in regions with less stringent regulations.
Alternatives to Coal
Renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower generate electricity without direct air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions. Natural gas, while still a fossil fuel, produces fewer pollutants and less CO
2
than coal when burned. Energy efficiency and demand-side management can further reduce the need for coal-fired power.
Conclusion
Coal is not good for the environment. Its extraction and use cause severe air and water pollution, contribute significantly to climate change, and pose serious risks to human health [1] [2] [4] . While pollution controls and policy changes have reduced its impact in some regions, coal remains one of the most environmentally harmful energy sources. Transitioning to cleaner alternatives is essential for protecting public health and the planet.
How to Learn More and Take Action
For detailed statistics on coal’s environmental impact, visit the U.S. Energy Information Administration website and search for “coal and the environment.” To explore health studies, consult resources from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and the Union of Concerned Scientists. For information on renewable energy options and energy efficiency programs, contact your local utility or state energy office, or visit the official websites of the U.S. Department of Energy and Environmental Protection Agency.
References
[2] U.S. Energy Information Administration (2023). Coal and the environment.
MORE FROM promohunterpro.com